What are the different components of a building? Did you just say, living room, dining room, bedroom, kitchen, bathroom?? Maybe, you are not alone. Majority of our people consider themselves too non technical to understand the details when it comes to constructing a building. We think that technical aspects of a building are for the engineer and the contractor to worry about. Well, come to think of it and it’s not really that hard..
Basic components of a building
After all it’s our home; we own it, so it’s we who should understand it better than any engineer or contractor.

Let’s simplify this a bit and look at the different components of a building, one at a time. For ease of understanding, let us divide the building into two parts. One that we see above the ground (which will be called the superstructure) and one that goes below the ground (that is called the substructure or foundation)
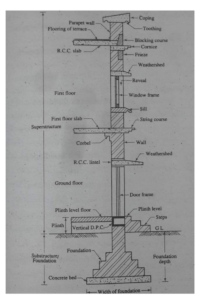
Substructure (Foundation)
Foundation is the most important aspect in any building construction. Choosing the right type of foundation is extremely significant and should be done with utmost caution. The strength of your proposed house is directly proportional to the strength of the foundation used. This in turn means that the number of floors your house can accommodate, the type of roofing to be used etc are all dependent on the type of foundation.
Now how do you choose the right type of foundation for your house?
Foundation type is usually determined by the kind of soil in your property and the strata below the ground. In other words, it is not just the quality of the topsoil that is important, but also the type of soil that lies beneath the topsoil. It is recommended to get the soil in your property tested scientifically before zeroing in on the foundation type. A standard soil testing report will reveal several inputs on the quality of the soil; like density, moisture content, presence of organic matter etc.
Once the soil test report is available, your structural engineer can decide on the type of foundation to be used. The most commonly used foundation types in Kerala conditions are
- Rubble Foundation
- Pillar Footing Foundation
- Raft Foundation(Strip Foundation) &
- Piling
Additional reading on the topic
Superstructure
We further divide the superstructure component of a building into 3 parts
- Plinth level
- Sill level
- Lintel level
Plinth level
In order to restrict the seepage of rainwater and mud into the house, it is customary to maintain the floor of the house at a certain height above the ground. A plinth is the base upon which the structure of the building rests . It raises the floor above the ground level and prevents seepage of rainwater into the building. The finished floor is called the plinth level floor and the level at which the floor is built is called the plinth level. In other words the plinth level is the part of the superstructure that lies between the natural ground level and the finished floor. The distance from the ground to the finished floor is called the plinth height. The plinth height should be a minimum of 300mm-450mm (usually at a height of 3-4 steps).
A damp proof course (DPC) is applied on the plinth level. This process minimizes the movement of moisture through the walls and the floor.
In short having a plinth level provides the following benefits
- Provides Damp proofing thereby protecting the house from moisture.
- Increases the aesthetic appeal of the house
- Acts as a supporting wall for the backfilling
- Transfers the load of the building from the superstructure to the foundation.
Sill level
The window sill level , commonly known as the sill level is the level from the finished floor till the base of the window. The height of the sill is a personal preference and depends on the type of room. For example, the sill level for bedrooms may be different from that for living rooms or bathrooms.
The windows are installed just above the sill level. The windows are surrounded by a frame, that is usually made of wood. This is known as the reveal. Apart from this you also place a weathershed to prevent the direct entry to rainwater into the building during the monsoons.
Lintel level
Lintel level is the level between the top portion of the window and the top slab. A concrete beam is usually placed at this level. The purpose of the concrete beam is to provide support to the walls above the doors, windows or any other opening. In order to obtain higher levels of strength, it is a good practice to use steel as a reinforcement to the concrete mixture. Since the bond between steel and concrete is strong, it is possible to place steel bars at tensile zones of the structure. This practice is called steel reinforcement and after the reinforcement, the concrete is called Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC).
Blockwork is done above at this level also to create the building walls.
Slab casting
Roof slab is cast over the lintel level. During this stage, a criss-cross framework of reinforcement steel is placed over the shuttering before the actual pouring of concrete is done. This is done to provide support to the concrete, which is a mixture of cement, river sand (or m- sand), blue metal, all in the right proportions and with special additives as required. Then the slab is allowed to ‘cure’ for a specified number of days to ensure its strength. In case of more floors, this process is repeated. After the curing period, walls of the first floor are raised and the above process is repeated.
Parapet wall
Additionally a parapet wall is constructed over the topmost floor. A parapet wall is a low protective wall along the edge of the balcony or the terrace. Once the brickwork is completed for the parapet wall, the top has to be capped or covered. This process is known as coping and is usually done by placing a layer of stone, terracotta, brick or concrete on top of the exposed wall. Coping helps to prevent water seepage to a very large extent.
Additional reading: Stages of building construction
Decorative components of a building
To provide additional support , engineers also suggest the use of a corbel, which is a piece of wood, stone or metal jutting from the wall. Though corbels were originally introduce to provide support to the walls, they also serve a decorative purpose. Furthermore, they can be styled in such a manner to enhance the interiors of the house.
A stringcourse, which is a horizontal band made of brick or stone is also used along the exterior of the wall as a decorative element in some constructions.
A frieze, which is a long stretch of painted or sculpted decorations usually placed above the eye level adorns the upper part of the building. A frieze is typical for the Persians and is not usually seen in residential constructions.
Cornice – This is a horizontal decorative moulding around the wall, just below the ceiling. A cornice can be placed above a door or window or along the top of a wall.
Blocking Course – It is the finishing course of a wall above a cornice that serves as a solid parapet. In addition to the decorative aspect, the building course serves as weights or forces on the cornice and prevents them from falling.
Corbel

Frieze

Cornice

Blocking Course

Hope this gave you a basic understanding of the various components of a building. If you have any further questions related to building construction, please feel free to get in touch with us. Our team would be happy to help!







