We have already seen the two kinds of foundations used in building construction – Shallow and Deep Foundation. We also saw the most basic type of shallow foundation – the rubble foundation. Now let’s look at another type of shallow foundation namely the Strip foundation or Strip Footing.
At times the size of the structure and/or the soil conditions might warrant the use of foundations that are more stable than the Rubble foundation. In other cases, the soil would be strong enough and the use of rubble foundation would be sufficient, but there could be water logging in the site which may cause erosion of the materials used for packing rubble. Also in waterlogged areas, the labour required for laying rubble foundation would be very high. Your structural engineer may suggest the use of strip foundation in this case. Strip foundation can also be used in conditions where rubble is not readily available.
What is Strip Foundation or Strip Footing?
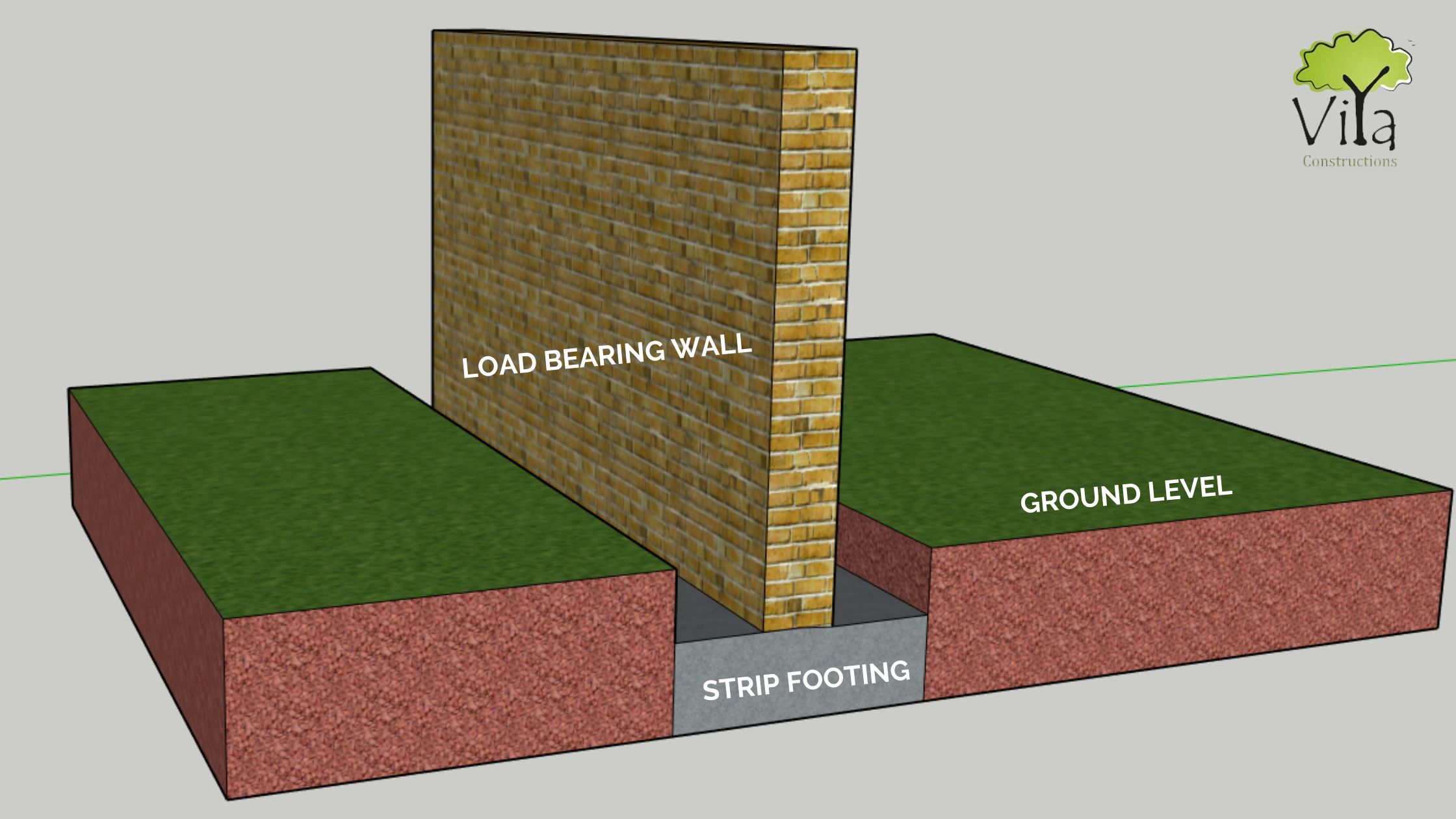
A strip footing is that in which a continuous strip of concrete is placed below the load-bearing walls. It spreads the weight of the load-bearing wall evenly across the total area of the soil. The footing can be made in either plain concrete or reinforced concrete.
When is Strip footing used?
Strip footing is commonly used as foundations for load-bearing walls; and when the soil has good bearing capacity. It is preferred for low rise to medium-rise residential buildings. Here a strip of concrete runs below the entire length of the wall, thereby distributing the load from the walls to the ground. This offers better stability to the building. For this reason, the width of the footing should be at least twice the width of the wall.
In some cases, strip foundations are used to support a row of closely spaced columns. In such a case a strip footing would be more economical than the spread footings that overlap each other.
If the bearing capacity of the soil is low, you may have to go for wider strip foundations. In such cases, plain concrete might not suffice. You will have to use reinforced concrete in such cases.
The exact width of the load-bearing wall and the footing is dependent on the soil condition. Your structural engineer should be able to guide you on this based on the soil test reports from your plot.
When should you not use a Strip foundation?
- When there are several columns in the building, with high localized loads, strip footing may not be appropriate. In such cases, choose an isolated footing or pad foundation.
- If the soil condition is weak, or when settlement is likely it is more appropriate to choose raft or mat foundation.
- When the bearing capacity of the soil is too weak to support the weight of the structure, choose deep foundations like pile foundations.
- For buildings taller than 3 or 4 storeys, deep foundations would be more appropriate than strip foundations
Step by step procedure – Strip Footing
- Identify the positions of the load-bearing walls.
- Excavate the site at these positions and form a trench. The trench should be central to the wall above.
- Pour in lean concrete.
- Erect the formwork and install the bottom main bars.
- Installation of column starter bars follow.
- Binders are used to tie the column starter bars.
- The next step is to install the upper main bars.
- This is followed by the installation of upper distribution bars.
- Now fill concrete into the formwork.
- Once the concrete sets, the formwork can be removed.
- The excavated material can be used for backfilling.



Types of Walls in Building Construction - Viya Constructions
[…] as load-bearing walls. Load-bearing walls are thicker than non load-bearing or partition walls. Strip foundation and load-bearing walls usually go hand in […]